在打包 APK 文件时,资源文件会借助 Android SDK 中的 aapt/aapt2 工具进行编译和链接。以 XML 类型的文件为例,会按照 AXML 的格式编译成一个二进制文件。关于 AXML 这个格式,并没找到详细的官方文档,但社区中有许多的开源工具,同时配合阅读 AOSP 源码 可以帮助了解该文件格式的结构。
提取 AndroidManifest.xml
以 APK 中必须包含的 AndroidManifest.xml 为例进行分析,你可以使用以下命令提取未解码的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件:
unzip demo.apk AndroidManifest.xml
文件结构
可借助 010 Editor 并使用 AndroidManifest.bt 模板协助分析,AXML 文件由多个 Chunk 组成,每个 Chunk 都有一个 Header 结构,该结构是共用的。
ResChunkHeader
文件内容通常以 0x00080003 开头,可以将它看作是 Magic Number。其中 0x0003 表示 Type 为 RES_XML_TYPE, 0x0008 表示 Header Size,紧跟着 4 个字节 0x0001775c (96092 个字节) 描述整个文件的大小(包含 Header 部分)。
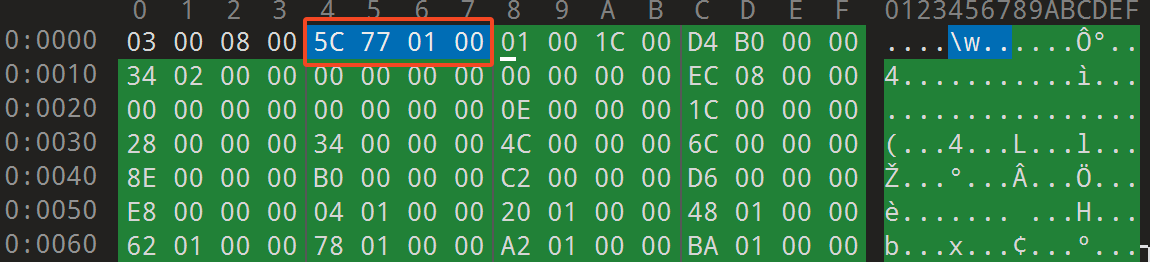
ResChunk_header
所有的 Chunk 都以 ResChunk_header 结构开头(包括前面的文件头和后续提及的其它类型的 Chunk),长度共计 8 个字节。前两个字节表示类型,紧跟着两个字节表示整个头部的大小,最后 4 个字节表示整个 Chunk 的大小。
/**
* Header that appears at the front of every data chunk in a resource.
*/
struct ResChunk_header
{
// Type identifier for this chunk. The meaning of this value depends
// on the containing chunk.
uint16_t type;
// Size of the chunk header (in bytes). Adding this value to
// the address of the chunk allows you to find its associated data
// (if any).
uint16_t headerSize;
// Total size of this chunk (in bytes). This is the chunkSize plus
// the size of any data associated with the chunk. Adding this value
// to the chunk allows you to completely skip its contents (including
// any child chunks). If this value is the same as chunkSize, there is
// no data associated with the chunk.
uint32_t size;
};--- title: "ResChunkHeader" --- packet-beta 0-15: "Type" 16-31: "Header Size" 32-63: "Chunk Size"
RES_STRING_POOL_TYPE
StringPool 中存放的是文件中的字符串,头部结构如下,共计 28 个字节。其中 ResChunk_header 在前面已经分析过了,其它字段请参考注释
struct ResStringPool_header
{
struct ResChunk_header header;
// Number of strings in this pool (number of uint32_t indices that follow
// in the data).
uint32_t stringCount;
// Number of style span arrays in the pool (number of uint32_t indices
// follow the string indices).
uint32_t styleCount;
// Flags.
enum {
// If set, the string index is sorted by the string values (based
// on strcmp16()).
SORTED_FLAG = 1<<0,
// String pool is encoded in UTF-8
UTF8_FLAG = 1<<8
};
uint32_t flags;
// Index from header of the string data.
uint32_t stringsStart;
// Index from header of the style data.
uint32_t stylesStart;
};--- title: "ResStringPoolHeader" --- packet-beta 0-31: "String Count" 32-63: "Style Count" 64-95: "Flags" 96-127: "String Start" 128-159: "Style Start"
实例
使用 hexdump 工具获取这段内容,
$ hexdump -C -s 0x08 -n 28 AndroidManifest.xml
00000008 01 00 1c 00 d4 b0 00 00 34 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 |........4.......|
00000018 00 00 00 00 ec 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 |............|
000000240x0100:type,对应常量RES_XML_FIRST_CHUNK_TYPE0x001c: 头部大小headerSize0x0000b0d4:chunk大小,不包含头部ResStringPool_header的大小0x00000234:stringCount,字符串的数量0x00000000:styleCount,style span arrays数量,目前不清楚什么是style span arrays0x00000000:flag,0x100表示字符串以UTF-8形式编码,0x0表示字符串内容已按字典序排列0x000008ec:stringsStart,存放字符串的起始位置的索引,该索引不包含最初的8字节文件头的长度,此处为2284,实际访问字符串应从第2292个字节开始,稍后会做演示。0x00000000:stylesStart同上。
Entries
在源码中并没有对该部分内容定义 struct,它的结构整体非常规整紧跟在 ResStringPool_header 之后,每 4 个字节存储对应字符串的在 Strings 中的 offset,共计 stringCount x 4 个字节。继续以前面的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件为示例,读取 Entries 的内容。
0x00000000:第一个字符串的offset,为00x0000000e:第二个字符串的offset,为14
$ hexdump -C -s 0x24 -n 8 AndroidManifest.xml
00000024 00 00 00 00 0e 00 00 00 |........|
0000002c关于字符串的起始位置和如何读取字符串会在 Strings 介绍。
Strings
和 Entries 一样源码中没有对该部分定义具体的 struct。
通过分析源代码的逻辑,可以确定 Strings 的结构分两种情况,一种为 UTF-16 一种为 UTF-8。UTF-16 支持最大长度为 0x7FFFFFFFU 个字节(不代表实际的字符数量)的字符串,UTF-8 支持最大长度为 0x7FFFU 个字节(不代表实际的字符数量)的字符串。关于这一点可从 decodeLength 方法了解
/**
* Strings in UTF-16 format have length indicated by a length encoded in the
* stored data. It is either 1 or 2 characters of length data. This allows a
* maximum length of 0x7FFFFFF (2147483647 bytes), but if you're storing that
* much data in a string, you're abusing them.
*
* If the high bit is set, then there are two characters or 4 bytes of length
* data encoded. In that case, drop the high bit of the first character and
* add it together with the next character.
*/
static inline base::expected<size_t, IOError> decodeLength(incfs::map_ptr<uint16_t>* str)
{
if (UNLIKELY(!*str)) {
return base::unexpected(IOError::PAGES_MISSING);
}
size_t len = str->value();
if ((len & 0x8000U) != 0) {
++(*str);
if (UNLIKELY(!*str)) {
return base::unexpected(IOError::PAGES_MISSING);
}
len = ((len & 0x7FFFU) << 16U) | str->value();
}
++(*str);
return len;
}
/**
* Strings in UTF-8 format have length indicated by a length encoded in the
* stored data. It is either 1 or 2 characters of length data. This allows a
* maximum length of 0x7FFF (32767 bytes), but you should consider storing
* text in another way if you're using that much data in a single string.
*
* If the high bit is set, then there are two characters or 2 bytes of length
* data encoded. In that case, drop the high bit of the first character and
* add it together with the next character.
*/
static inline base::expected<size_t, IOError> decodeLength(incfs::map_ptr<uint8_t>* str)
{
if (UNLIKELY(!*str)) {
return base::unexpected(IOError::PAGES_MISSING);
}
size_t len = str->value();
if ((len & 0x80U) != 0) {
++(*str);
if (UNLIKELY(!*str)) {
return base::unexpected(IOError::PAGES_MISSING);
}
len = ((len & 0x7FU) << 8U) | str->value();
}
++(*str);
return len;
}Strings 的内容就紧跟在 Entries 之后,所以读取字符串时分为两步:
- 计算字符串起始位置:从
Entries获取offset,并根据String的起始位置计算字符串所在起始位置。 - 解析字符串内容。
由于 Entries 的长度就是 stringCount x 4,可以很轻松的找到 Strings 的起始位置。参考前面的示例,Entries 的长度是 564*4=2256。
使用 hexdump 读取 Strings 的内容,偏移为 0x8F4
$ hexdump -C -s 0x8F4 -n 32 xiaola/AndroidManifest.xml
000008f4 05 00 74 00 68 00 65 00 6d 00 65 00 00 00 05 00 |..t.h.e.m.e.....|
00000904 6c 00 61 00 62 00 65 00 6c 00 00 00 04 00 69 00 |l.a.b.e.l.....i.|
00000914以读取第二个字符串的为例,已知它的 offset 为 0x0000000e=14。读取第一个字符为 0x0005 代表长度,即 5;接着读取后面的 5 个字符组成字符串,即 label,最后是终止字符 0x0000。
--- title: "String" --- packet-beta 0-15: "String Size" 16-30: "String (variable length)" 31: "NULL"
RES_XML_RESOURCE_MAP_TYPE
StringPool 之后可能会存在一个 Chunk,用于存放一个数组,称为 Resource Map。根据文档中的注释,该数组存储的是 StringPool 与资源标识符的映射关系。该 Chunk 包含一个 ResChunk_header 其后跟随的是存储的数据,Type 类型为 RES_XML_RESOURCE_MAP_TYPE=0x180
在源码中,对于 header 后的数据字段仅初始两个成员字段:
- mResIds:指向数据字段的第一个元素(类型 uint32,共
4个字节),应该只是用于存储索引,便于后续查找 - mNumResIds:资源
id的数量,数据字段的长度除4
mResIds = (const uint32_t*)
(((const uint8_t*)chunk)+dtohs(chunk->headerSize));
mNumResIds = (dtohl(chunk->size)-dtohs(chunk->headerSize))/sizeof(uint32_t);
继续看示例,其中 80 01 08 00 e4 00 00 00 为 header 部分
- type:
RES_XML_RESOURCE_MAP_TYPE=0x180 - headerSize:
0x0008 - size:
0x000000e4
后门每 4 个字节存储一个资源 id,这个数值后续如何使用还不确定。
$ hexdump -C -s 0xB0DC -n 32 AndroidManifest.xml
0000b0dc 80 01 08 00 e4 00 00 00 00 00 01 01 01 00 01 01 |................|
0000b0ec 02 00 01 01 03 00 01 01 06 00 01 01 07 00 01 01 |................|RES_XML_TYPE
Chunk 的 header 中的 Type 值处于 0x0100 和 0x017f 的都称为 RES_XML_TYPE,共计 7 个。
RES_XML_FIRST_CHUNK_TYPE = 0x0100,
RES_XML_START_NAMESPACE_TYPE = 0x0100,
RES_XML_END_NAMESPACE_TYPE = 0x0101,
RES_XML_START_ELEMENT_TYPE = 0x0102,
RES_XML_END_ELEMENT_TYPE = 0x0103,
RES_XML_CDATA_TYPE = 0x0104,
RES_XML_LAST_CHUNK_TYPE = 0x017f,
RES_XML_Header
RES_XML_TYPE 类型的 Chunk 头部结构由 ResXMLTree_node 定义,所有的 RES_XML_TYPE 类型的 Chunk 都以该结构开头。其中包含行号和 comment 字符串的索引,用于从 StringPool 中获取字符串,共计 16 个字节。如果 comment 的值为 0xffffffff 则表示不存在。
/**
* Basic XML tree node. A single item in the XML document. Extended info
* about the node can be found after header.headerSize.
*/
struct ResXMLTree_node
{
struct ResChunk_header header;
// Line number in original source file at which this element appeared.
uint32_t lineNumber;
// Optional XML comment that was associated with this element; -1 if none.
struct ResStringPool_ref comment;
};
/**
* Reference to a string in a string pool.
*/
struct ResStringPool_ref
{
// Index into the string pool table (uint32_t-offset from the indices
// immediately after ResStringPool_header) at which to find the location
// of the string data in the pool.
uint32_t index;
};--- title: "RES_XML_Header" --- packet-beta 0-15: "Type" 16-31: "Header Size" 32-63: "Chunk Size" 64-95: "Line Number" 96-127: "Comment (reference id of string)"
RES_XML_START_NAMESPACE_TYPE
Header 中 Type 字段值为 0x0100,数据体由 ResXMLTree_namespaceExt 定义,2 个字段共 8 个字节,算上 header 共 24 个字节。该结构体同时表示 start/end 节点,即 <>/</>
/**
* Extended XML tree node for namespace start/end nodes.
* Appears header.headerSize bytes after a ResXMLTree_node.
*/
struct ResXMLTree_namespaceExt
{
// The prefix of the namespace.
struct ResStringPool_ref prefix;
// The URI of the namespace.
struct ResStringPool_ref uri;
};
来看示例
$ hexdump -C -s 0xB1C0 -n 24 AndroidManifest.xml
0000b1c0 00 01 10 00 18 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 ff ff ff ff |................|
0000b1d0 7f 00 00 00 0b 02 00 00 |........|0x0000007f:namespacePrefixID, ns prefix 在 StringPool 中的索引0x0000020b:namespaceUriID,ns uri 在 StringPool 中的索引
获取 id 之后可从 StringPool 获取对应的字符串。
RES_XML_START_ELEMENT_TYPE
Header 中 Type 字段值为 0x0102,数据体部分包含 ResXMLTree_attrExt 和 0 至多个 ResXMLTree_attribute。
ResXMLTree_attrExt
在源码中定义了结构体 ResXMLTree_attrExt,用于描述 Start Tag 的元数据,长度为 20 个字节
/**
* Extended XML tree node for start tags -- includes attribute
* information.
* Appears header.headerSize bytes after a ResXMLTree_node.
*/
struct ResXMLTree_attrExt
{
// String of the full namespace of this element.
struct ResStringPool_ref ns;
// String name of this node if it is an ELEMENT; the raw
// character data if this is a CDATA node.
struct ResStringPool_ref name;
// Byte offset from the start of this structure where the attributes start.
uint16_t attributeStart;
// Size of the ResXMLTree_attribute structures that follow.
uint16_t attributeSize;
// Number of attributes associated with an ELEMENT. These are
// available as an array of ResXMLTree_attribute structures
// immediately following this node.
uint16_t attributeCount;
// Index (1-based) of the "id" attribute. 0 if none.
uint16_t idIndex;
// Index (1-based) of the "class" attribute. 0 if none.
uint16_t classIndex;
// Index (1-based) of the "style" attribute. 0 if none.
uint16_t styleIndex;
};来看示例
$ hexdump -C -s 0xB1D8 -n 36 AndroidManifest.xml
0000b1d8 02 01 10 00 b0 00 00 00 02 00 00 00 ff ff ff ff |................|
0000b1e8 ff ff ff ff 13 02 00 00 14 00 14 00 07 00 00 00 |................|
0000b1f8 00 00 00 00 |....|0x0102:type,类型0x0010:headerSize头部长度0x000000b0:size整个 Chunk 块的长度0x00000002:lineNumber行号0xffffffff:comment在 StringPool 中的索引0xffffffff:ns在 StringPool 中的索引0x00000213:name在 StringPool 中的索引0x0014:attributeStart当前结构与attributes的起始位置的offset0x0014:attributeSize表示ResXMLTree_attribute结构的大小,20个字节0x0007:attributeCount表示attributes的个数0x0000:idIndex“id” 属性的索引,0表示未使用该属性0x0000:classIndex“class” 属性的索引0x0000:styleIndex“style” 属性的索引
--- title: "ResXMLTree Attribute Extension" --- packet-beta 0-31: "Namespace ID" 32-63: "Element Name ID" 64-79: "Attribute Start" 80-95: "Attribute Size" 96-111: "ID Index" 112-127: "Class Index" 128-143: "Style Index"
ResXMLTree_attribute
具体的属性值由结构体 ResXMLTree_attribute 定义共 4 个字段,整体长度为 20 个字节,其中 Res_value 由另一个结构体定义,长度为 6 个字节。属性的数量由 ResXMLTree_attrExt 中的 attributeSize 定义。
struct ResXMLTree_attribute
{
// Namespace of this attribute.
struct ResStringPool_ref ns;
// Name of this attribute.
struct ResStringPool_ref name;
// The original raw string value of this attribute.
struct ResStringPool_ref rawValue;
// Processesd typed value of this attribute.
struct Res_value typedValue;
};
/**
* Representation of a value in a resource, supplying type
* information.
*/
struct Res_value
{
// Number of bytes in this structure.
uint16_t size;
// Always set to 0.
uint8_t res0;
// Type of the data value.
enum : uint8_t {
// The 'data' is either 0 or 1, specifying this resource is either
// undefined or empty, respectively.
TYPE_NULL = 0x00,
// The 'data' holds a ResTable_ref, a reference to another resource
// table entry.
TYPE_REFERENCE = 0x01,
// The 'data' holds an attribute resource identifier.
TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = 0x02,
// The 'data' holds an index into the containing resource table's
// global value string pool.
TYPE_STRING = 0x03,
// The 'data' holds a single-precision floating point number.
TYPE_FLOAT = 0x04,
// The 'data' holds a complex number encoding a dimension value,
// such as "100in".
TYPE_DIMENSION = 0x05,
// The 'data' holds a complex number encoding a fraction of a
// container.
TYPE_FRACTION = 0x06,
// The 'data' holds a dynamic ResTable_ref, which needs to be
// resolved before it can be used like a TYPE_REFERENCE.
TYPE_DYNAMIC_REFERENCE = 0x07,
// The 'data' holds an attribute resource identifier, which needs to be resolved
// before it can be used like a TYPE_ATTRIBUTE.
TYPE_DYNAMIC_ATTRIBUTE = 0x08,
// Beginning of integer flavors...
TYPE_FIRST_INT = 0x10,
// The 'data' is a raw integer value of the form n..n.
TYPE_INT_DEC = 0x10,
// The 'data' is a raw integer value of the form 0xn..n.
TYPE_INT_HEX = 0x11,
// The 'data' is either 0 or 1, for input "false" or "true" respectively.
TYPE_INT_BOOLEAN = 0x12,
// Beginning of color integer flavors...
TYPE_FIRST_COLOR_INT = 0x1c,
// The 'data' is a raw integer value of the form #aarrggbb.
TYPE_INT_COLOR_ARGB8 = 0x1c,
// The 'data' is a raw integer value of the form #rrggbb.
TYPE_INT_COLOR_RGB8 = 0x1d,
// The 'data' is a raw integer value of the form #argb.
TYPE_INT_COLOR_ARGB4 = 0x1e,
// The 'data' is a raw integer value of the form #rgb.
TYPE_INT_COLOR_RGB4 = 0x1f,
// ...end of integer flavors.
TYPE_LAST_COLOR_INT = 0x1f,
// ...end of integer flavors.
TYPE_LAST_INT = 0x1f
};
uint8_t dataType;
// Structure of complex data values (TYPE_UNIT and TYPE_FRACTION)
enum {
// Where the unit type information is. This gives us 16 possible
// types, as defined below.
COMPLEX_UNIT_SHIFT = 0,
COMPLEX_UNIT_MASK = 0xf,
// TYPE_DIMENSION: Value is raw pixels.
COMPLEX_UNIT_PX = 0,
// TYPE_DIMENSION: Value is Device Independent Pixels.
COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP = 1,
// TYPE_DIMENSION: Value is a Scaled device independent Pixels.
COMPLEX_UNIT_SP = 2,
// TYPE_DIMENSION: Value is in points.
COMPLEX_UNIT_PT = 3,
// TYPE_DIMENSION: Value is in inches.
COMPLEX_UNIT_IN = 4,
// TYPE_DIMENSION: Value is in millimeters.
COMPLEX_UNIT_MM = 5,
// TYPE_FRACTION: A basic fraction of the overall size.
COMPLEX_UNIT_FRACTION = 0,
// TYPE_FRACTION: A fraction of the parent size.
COMPLEX_UNIT_FRACTION_PARENT = 1,
// Where the radix information is, telling where the decimal place
// appears in the mantissa. This give us 4 possible fixed point
// representations as defined below.
COMPLEX_RADIX_SHIFT = 4,
COMPLEX_RADIX_MASK = 0x3,
// The mantissa is an integral number -- i.e., 0xnnnnnn.0
COMPLEX_RADIX_23p0 = 0,
// The mantissa magnitude is 16 bits -- i.e, 0xnnnn.nn
COMPLEX_RADIX_16p7 = 1,
// The mantissa magnitude is 8 bits -- i.e, 0xnn.nnnn
COMPLEX_RADIX_8p15 = 2,
// The mantissa magnitude is 0 bits -- i.e, 0x0.nnnnnn
COMPLEX_RADIX_0p23 = 3,
// Where the actual value is. This gives us 23 bits of
// precision. The top bit is the sign.
COMPLEX_MANTISSA_SHIFT = 8,
COMPLEX_MANTISSA_MASK = 0xffffff
};
// Possible data values for TYPE_NULL.
enum {
// The value is not defined.
DATA_NULL_UNDEFINED = 0,
// The value is explicitly defined as empty.
DATA_NULL_EMPTY = 1
};
// The data for this item, as interpreted according to dataType.
typedef uint32_t data_type;
data_type data;
void copyFrom_dtoh(const Res_value& src);
};来看示例
$ hexdump -C -s 0xB1FC -n 20 AndroidManifest.xml
0000b1fc 0b 02 00 00 1c 00 00 00 ff ff ff ff 08 00 00 10 |................|
0000b20c 98 08 00 00 |....|0x0000020b:ns在 StringPool 中的 id0x0000001c:name属性名在 StringPool 中的 id0xffffffff:rawValue属性值的字符串表示在 StringPool 在 StringPool 中的 id0x0008:size结构体Res_value的大小0x00:res0固定为00x10:dataType属性值的数据类型0x00000898:data属性值,根据dataType的类型来解析该部分数据
--- title: "ResXMLTree Attribute" --- packet-beta 0-31: "Namespace StringPool ID" 32-63: "Attribute Name StringPool ID" 64-95: "Raw Value StringPool ID" 96-111: "Size" 112-119: "Res0" 120-127: "Data Type" 128-159: "Data"
RES_XML_CDATA_TYPE
Header 中 Type 字段值为 0x0104
ResXMLTree_cdataExt
数据体结构由 ResXMLTree_cdataExt 定义,长度为 12 字节,Res_value 前面已介绍,这里略过。data 存储这 CDATA 内的字符串在 StringPool 的索引。
/**
* Extended XML tree node for CDATA tags -- includes the CDATA string.
* Appears header.headerSize bytes after a ResXMLTree_node.
*/
struct ResXMLTree_cdataExt
{
// The raw CDATA character data.
struct ResStringPool_ref data;
// The typed value of the character data if this is a CDATA node.
struct Res_value typedData;
};
--- title: "ResXMLTree CDATA" --- packet-beta 0-31: "Raw CDATA StringPool ID" 32-47: "Size" 48-54: "Res0" 55-63: "Data Type" 64-95: "Data"
RES_XML_END
从前面知道 END 节点有两类 RES_XML_END_NAMESPACE_TYPE 和 RES_XML_END_ELEMENT_TYPE, 源码中在进行 XML 内容读取时,对于 </> 一类的标签并不关注,会跳过该类 Node 的处理。
std::unique_ptr<XmlResource> Inflate(const void* data, size_t len, std::string* out_error) {
TRACE_CALL();
// We import the android namespace because on Windows NO_ERROR is a macro, not
// an enum, which causes errors when qualifying it with android::
using namespace android;
std::unique_ptr<XmlResource> xml_resource = util::make_unique<XmlResource>();
std::stack<Element*> node_stack;
std::unique_ptr<Element> pending_element;
ResXMLTree tree;
if (tree.setTo(data, len) != NO_ERROR) {
if (out_error != nullptr) {
*out_error = "failed to initialize ResXMLTree";
}
return {};
}
ResXMLParser::event_code_t code;
while ((code = tree.next()) != ResXMLParser::BAD_DOCUMENT && code != ResXMLParser::END_DOCUMENT) {
std::unique_ptr<Node> new_node;
switch (code) {
// ...
case ResXMLParser::END_NAMESPACE:
break;
case ResXMLParser::END_TAG:
CHECK(!node_stack.empty());
node_stack.pop();
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "unhandled XML chunk type";
break;
}
}
return xml_resource;
}RES_XML_END_NAMESPACE_TYPE 的结构在 RES_XML_START_NAMESPACE_TYPE 中已经介绍过了。RES_XML_END_ELEMENT_TYPE 数据体的结构和 RES_XML_END_NAMESPACE_TYPE 是一样的,这里就不细说了。
/**
* Extended XML tree node for element start/end nodes.
* Appears header.headerSize bytes after a ResXMLTree_node.
*/
struct ResXMLTree_endElementExt
{
// String of the full namespace of this element.
struct ResStringPool_ref ns;
// String name of this node if it is an ELEMENT; the raw
// character data if this is a CDATA node.
struct ResStringPool_ref name;
};
源码分析
Info
从源码层面了解以下命令的执行流程
aapt2 d xmltree test.apk --file AndroidManifest.xml
涉及的代码文件较多,这里仅简要概括处理流程,感兴趣可以自己阅读。文件资源的 Dump 大概包含以下步骤:
- APK 文件加载
- 资源文件加载与解析
- 资源文件打印
APK 文件加载
在 tools/aapt2/cmd/Dump.h#34 定义了类 DumpApkCommand,其中包含一个方法 Action 用于处理 APK 文件加载
int Action(const std::vector<std::string>& args) final {
if (args.size() < 1) {
diag_->Error(android::DiagMessage() << "No dump apk specified.");
return 1;
}
bool error = false;
for (auto apk : args) {
auto loaded_apk = LoadedApk::LoadApkFromPath(apk, diag_);
if (!loaded_apk) {
error = true;
continue;
}
error |= Dump(loaded_apk.get());
}
return error;
}LoadedApk::LoadApkFromPath 方法会返回一个 LoadedApk 指针并交由 Dump 进行后续操作。该方法会探测 APK 文件类型是 Binary/Protocol Buf。
资源文件加载与解析
相关逻辑位于 tools/aapt2/dump/DumpManifest.cpp#3104
int DumpManifest(LoadedApk* apk, DumpManifestOptions& options, text::Printer* printer,
android::IDiagnostics* diag) {
ManifestExtractor extractor(apk, options);
if (!extractor.Extract(diag)) {
return 1;
}
return extractor.Dump(printer) ? 0 : 1;
}跟入 Extract() 方法,该方法调用 LoadXml("AndroidManifest.xml", diag) 加载并解析 AndroidManifest.xml 文件内容,返回一个 XmlResource 对象
bool ManifestExtractor::Extract(android::IDiagnostics* diag) {
// Load the manifest
doc_ = apk_->LoadXml("AndroidManifest.xml", diag);
if (doc_ == nullptr) {
diag->Error(android::DiagMessage() << "failed to find AndroidManifest.xml");
return false;
}资源文件打印
在 DumpManifest() 方法中解析成功后,调用 extractor.Dump(printer) 进行打印。
参考
- https://github.com/google/android-classyshark/blob/master/ClassySharkWS/src/com/google/classyshark/silverghost/translator/xml/XmlDecompressor.java 「android-classyshark 工具中的实现 XmlDecompressor.java」
- https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/manifest/manifest-intro 「AndroidManifest.xml 文件结构」